Connect Amperity Bridge to Snowflake¶
Amperity Bridge for Snowflake is a first-class integration that uses secure data sharing to enable bi-directional data access between Amperity and Snowflake without copying data or scheduling ETL workloads.
What is Secure Data Sharing?
Secure Data Sharing enables data sharing between Snowflake accounts without copying or transferring data and instead relies on the services layer and metadata store within Snowflake. Your brand controls what data will be made available to Amperity directly from within your brand’s Snowflake account.
Tip
Amperity Bridge for Snowflake shares data directly with Snowflake. A bridge does not require a courier or a database export to be configured. A bridge can be configured to run automatically as part of any scheduled workflow.
If your brand is using BI Connect to make data available in Snowflake your brand should consider moving the BI Connect workflow to Amperity Bridge. This increases the speed at which This allows your brand to self-service the data that is shared between Amperity and Snowflake directly from within your Snowflake account.
Data types¶
Most Snowflake data types are supported by Amperity Bridge.
Important
If an upstream data type changes, edit the bridge in Amperity, accept the changes, and then save and sync the bridge.
Warning
Complex types–arrays, objects, and maps–must have defined schemas.
The following table describes how Snowflake data types map to Amperity data types.
Snowflake data type |
Amperity data type |
|---|---|
|
A sequence of elements with the type of Warning A semi-structured ARRAY data type is unsupported. Use data type coversion to cast or coerce data in a semi-structured ARRAY into fully structured data before sharing it with Amperity Bridge. |
Array An ordered list of zero or more elements of non-array values by field name and value. Fields within an Array must contain values for data types supported by Amperity. Note Only fully structured ARRAY data types are supported. |
|
Synonymous with VARBINARY . |
Warning The Snowflake BINARY data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with BINARY data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A value that can be TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. |
Boolean A value that can be TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. |
|
Synonymous with VARCHAR, except the default length is VARCHAR(1). |
String A string of characters. |
|
Date values with no time element. |
Date An ISO-8601 compliant date value, such as a birthdate. For example:
|
|
An alias for TIMESTAMP_NTZ. |
See TIMESTAMP. |
|
A reference to a file in an internal or external stage. |
Warning The Snowflake FILE data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with FILE data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A double-precision (64 bit) IEEE 754 floating-point number. Note Synonymous with DOUBLE, DOUBLE PRECISION, FLOAT, FLOAT4, FLOAT8, and REAL data types. |
Float A floating point number. For example:
|
|
A collection of points, linestrings, and polygons that represent a set or subset of the surface of the Earth. |
Warning The Snowflake GEOGRAPHY data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with GEOGRAPHY data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A pairs of real numbers that represent features in a planar–Euclidean and Cartesian–coordinate system. |
Warning The Snowflake GEOMETRY data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with GEOMETRY data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A set of key-value pairs. Each pair must have a data type that maps to a supported Amperity data type. Warning A MAP can have value types for ARRAY or OBJECT. Use data type coversion to cast or coerce ARRAY and OBJECT value types within a MAP data type into fully structured data before sharing it with Amperity Bridge. |
Map A set of key-value pairs that map to supported Amperity data types. Note Only MAP data types with fully structured value types are supported. |
|
A number with up to 38 digits without precision and scale. Note Synonymous with BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
A number with up to 38 digits and precision and scale. Default precision and scale is (38,0). Note Synonymous with DECIMAL and NUMERIC data types. |
Decimal (p,s) A fixed point number, such as for prices or message sizes. The number of characters in the decimal value is configurable. For example:
|
|
A container of ordered fields. Fields within an OBJECT must contain values for data types supported by Amperity. Warning A semi-structured OBJECT data type is unsupported. Use data type coversion to cast or coerce data in a semi-structured OBJECT into fully structured data before sharing it with Amperity Bridge. |
Struct A container of ordered fields by name and type. Note Only fully structured OBJECT data types are supported. |
|
Snowflake allows ARRAY, OBJECT, and VARIANT data types to be semi-structured. |
Warning Semi-structured data types are unsupported. Use data type coversion to cast or coerce into fully structured data before sending data to Amperity Bridge. |
|
Time data stored as |
String A string of characters that represents |
|
A timestamp, including UTC time, UTC time with an offset, or a time with a specified precision. Note Synonymous with TIMESTAMP_LTZ, TIMESTAMP_NTZ, and TIMESTAMP_TZ. |
Datetime ISO-8601 compliant date and time values, such as a purchase or transaction, the time at which data was last updated, or a campaign launch date. For example:
|
|
A string of Unicode UTF-8 characters. Default length is 16777216 bytes. Maximum length is 134217728 bytes. Note Synonymous with STRING and TEXT . |
String A sequence of characters, such as first and last names, email addresses, physical addresses, UUIDs and other IDs, phone numbers, ZIP codes, product names, and descriptions. May be empty. For example:
|
|
A VARIANT value stores values of any type, including OBJECT and ARRAY, and is an unsupported semi-structured data type . |
Warning The Snowflake VARIANT data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with VARIANT data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A data type for encoding and processing vectors. |
Warning The Snowflake VECTOR data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with VECTOR data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
From Snowflake¶
A connection between Snowflake to Amperity requires configuration steps to be made in both Amperity and Snowflake.
Get details¶
Before you can create inbound sharing between Snowflake and Amperity you need to collect the following information.

|
The organization name and account name for your brand’s Snowflake account. An organization is a first-class object in Snowflake that links accounts and allows the use of secure data sharing. The unique name of an account that exists within your brand’s Snowflake organization. Tip To find your organization name and account name use Snowsight. Open the account selector and browse to the account for which Amperity Bridge will be configured. Hover over the account name to view additional details, and then copy the account identifier. The copied identifier contains both organization and account name in the format organization-name.account-name. |

|
The region that hosts your Snowflake account. Use the CURRENT_REGION argument in Snowflake to return the value for your region. |

|
Before you can configure Amperity Bridge for data sharing with Snowflake you must create a share in Snowflake, add a secure share identifier to that share, identify the correct account locator, and then add the Amperity account locator ID to the share. Use the CURRENT_ACCOUNT argument in Snowflake to return the locator ID for your Snowflake account. Important Secure data sharing should only share secure views with Amperity. |

|
A secure share identifier in Snowflake is a unique string–A-Z, 0-9, $, and _ (underscores)–that is added when creating a share. This string must configured in Amperity to enable the bridge. Copy the secure share identifier from the Snowflake user interface, and then share the identifier with the individual who will configure Amperity for secure data sharing with Snowflake. |
Configure Snowflake¶
Before you can configure Amperity Bridge for data sharing with Snowflake you must create a share in Snowflake, add a secure share identifier to that share, and then identify the correct account locator.
Configure secure views¶
Secure data sharing should only share secure views with Amperity. Amperity recommends that all views that are shared with Amperity be configured as secure views in Snowflake.
Alternatively, your brand may choose to configure Snowflake to allow sharing of non-secure views with Amperity.
Amperity account locator IDs¶
Snowflake must be configured for the correct account locator IDs used by Amperity. Account locator IDs are specific to the stack in which your Amperity tenant is provisioned and the region ID in which your Snowflake account resides.
Note
Outbound queries run faster when your Snowflake account and Amperity tenant storage are hosted in the same region. Outbound queries run slower when your Snowflake account and Amperity tenant storage are hosted in different regions.
For example, if your Amperity tenant storage is hosted on azure_eastus2 and you host your Snowflake account on azure_westus2, queries will be slower than if both were hosted on azure_eastus2.
Amperity stack |
Snowflake region |
Account locator |
|---|---|---|
aws-prod |
aws_us_east_1 |
MVB61607 |
aws-prod |
aws_us_east_2 |
BL95184 |
aws-prod |
gcp_us_east4 |
YU29648 |
aws-prod |
aws_us_west_2 |
GUB98973 |
aws-prod |
azure_eastus2 |
JTA41525 |
aws-prod |
azure_westus2 |
PZ39828 |
aws-prod-cc1 |
aws_us_west_2 |
EXB14788 |
az-prod |
azure_centralus |
MC75461 |
az-prod |
azure_eastus2 |
DSA38111 |
az-prod |
aws_us_west_2 |
BCB42530 |
az-prod |
azure_australiaeast |
MD18696 |
az-prod |
azure_westeurope |
RN08588 |
az-prod |
azure_australiaeast |
MD18696 |
az-prod-en1 |
azure_australiaeast |
TD45616 |
az-prod-en1 |
azure_westeurope |
KV75952 |
Important
If the account ID / region ID pair does not exist in your stack please contact Amperity Support.
Add inbound bridge¶
Configure an inbound bridge to connect Snowflake with Amperity.
To add an inbound bridge

|
Open the Sources page. Under Inbound shares click Add bridge. Choose Snowflake. 
This opens the Add bridge dialog box. 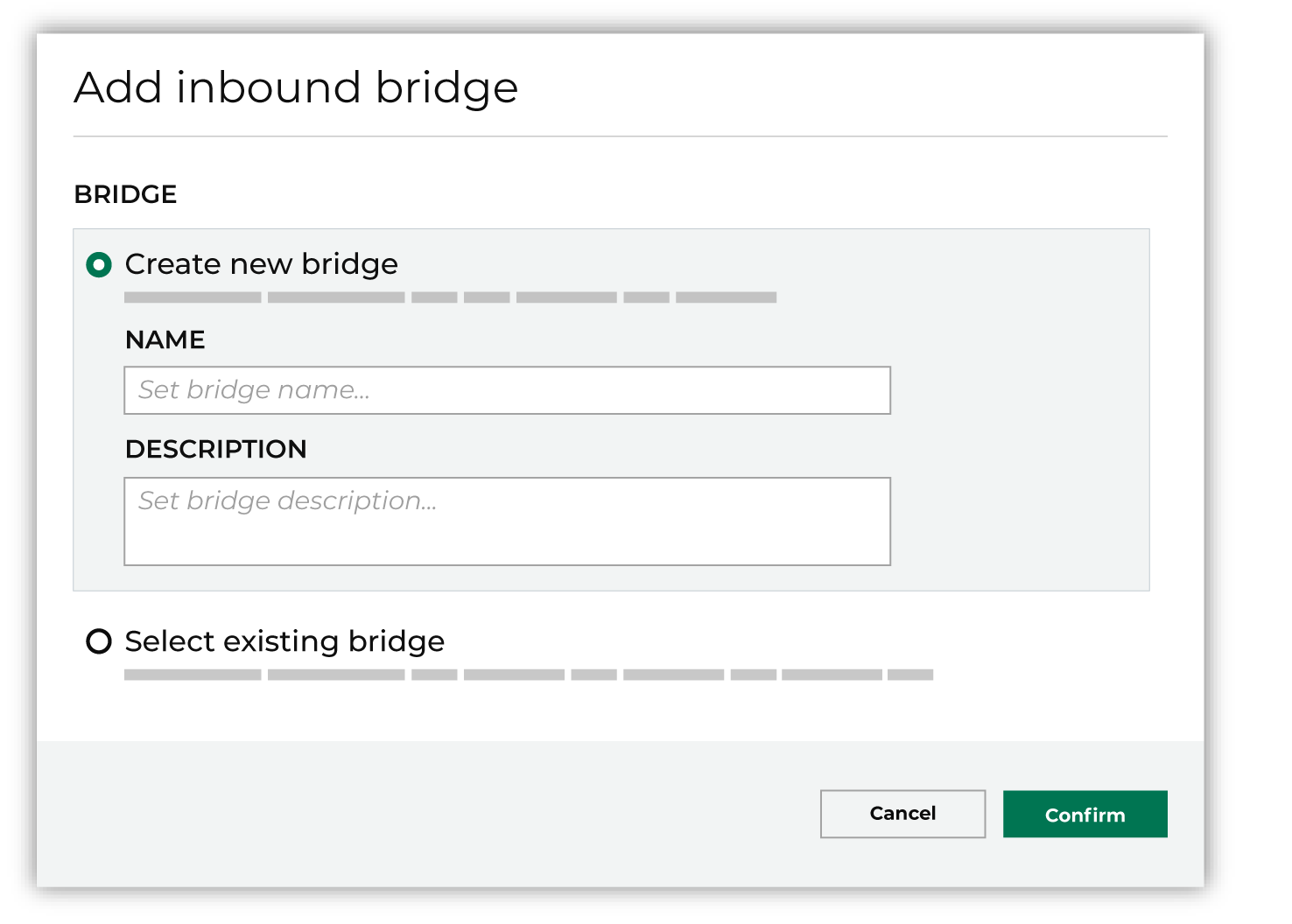
Add a name and description for the bridge or select an existing bridge, and then click Confirm. |

|
Configure the organization, account name, and region. An organization is a first-class object in Snowflake that links accounts and allows the use of secure data sharing. The unique name of an account that exists within your brand’s Snowflake organization. The region that hosts your Snowflake account. Use the CURRENT_REGION argument in Snowflake to return the value for your region. |

|
Add the Secure Share Identifier. When finished, click Continue. This opens the Select tables dialog box. |

|
Use the Select tables dialog box to select any combination of schemas and tables to be connected to Amperity. 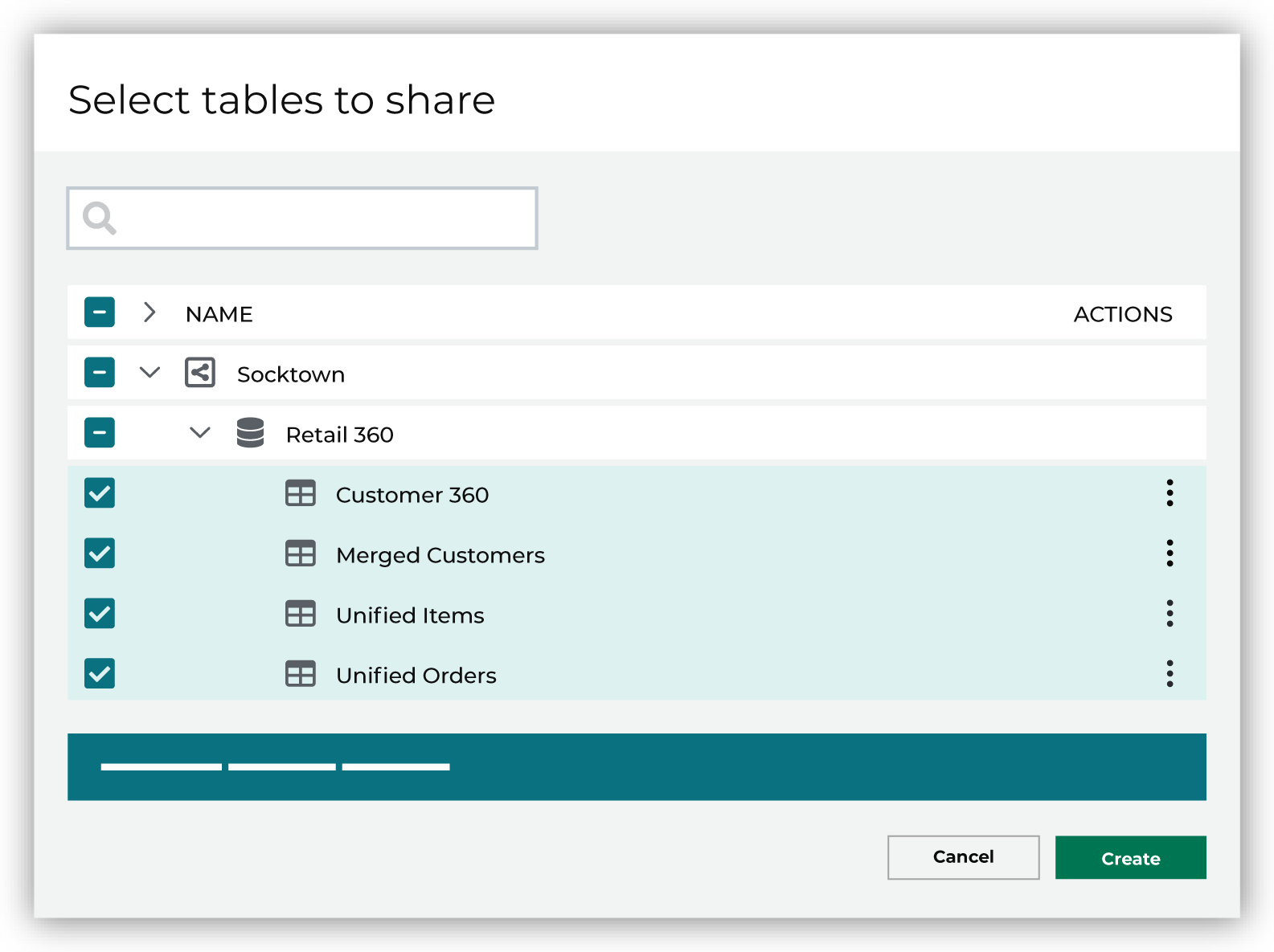
If you select a schema, all tables in that schema will be connected. Any new tables added later need to be manually added to the connection. When finished, click Next. This opens the Domain table mapping dialog box. |

|
Map the tables that are connected from Snowflake to domain tables in Amperity. 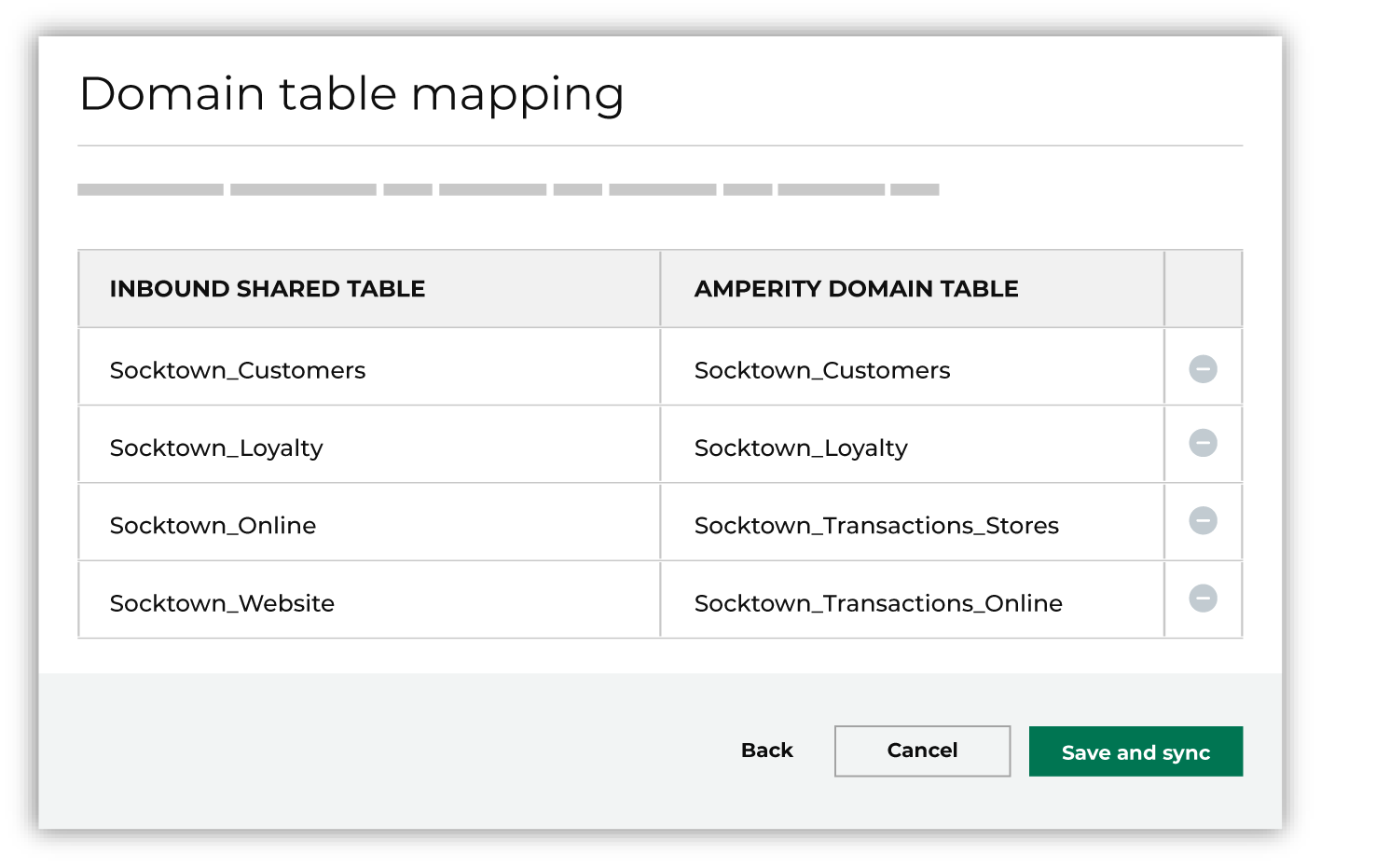
Tables that are connected with Amperity are added as domain tables.
Tip Use a custom domain table to assign primary keys, apply semantic tags, and shape data within connected tables to support any of your Amperity workflows. When finished, click Save and sync. This will start a workflow that synchronizes data from Snowflake to Amperity and creates the mapped domain table names. You can manually sync tables that are connected with Amperity using the Sync option from the Actions menu for the inbound bridge. |
To Snowflake¶
A connection between Amperity and Snowflake requires configuration steps to be made in both Amperity and Snowflake.
Note
Configuration state for an outbound bridge is not copied from production to a sandbox. An outbound bridge must be configured within a sandbox.
Get details¶
Before you can create outbound sharing between Snowflake and Amperity you need to collect the following information.

|
The organization name and account name for your brand’s Snowflake account. An organization is a first-class object in Snowflake that links accounts and allows the use of secure data sharing. The unique name of an account that exists within your brand’s Snowflake organization. Tip To find your organization name and account name use Snowsight. Open the account selector and browse to the account for which Amperity Bridge will be configured. Hover over the account name to view additional details, and then copy the account identifier. The copied identifier contains both organization and account name in the format organization-name.account-name. |

|
The region that hosts your Snowflake account. Use the CURRENT_REGION argument in Snowflake to return the value for your region. |

|
A user with the ACCOUNTADMIN role must create a database in Snowflake using the data that was shared from Amperity. |
Add outbound bridge¶
Configure an outbound bridge to connect with Snowflake.
To add an outbound bridge

|
Open the Destinations page. Select the Outbound shares tab, and then click Add bridge. Choose Snowflake. This opens the Create bridge dialog box. |

|
Add a name and description for the bridge or select an existing bridge. Configure the organization, account name, and region. An organization is a first-class object in Snowflake that links accounts and allows the use of secure data sharing. The unique name of an account that exists within your brand’s Snowflake organization. The region that hosts your Snowflake account. Use the CURRENT_REGION argument in Snowflake to return the value for your region. Click Next, after which you will select the tables to be shared with Snowflake. |
Configure Snowflake¶
After tables have been shared you need to create a database in Snowflake using the data that was shared from Amperity.
To create a database in Snowflake from shared data

|
Access the consumer listings that are available in your Snowflake account . From the Snowsight user interface in Snowflake, expand Data Products, then expand Private Sharing, and then find the direct share that was created for sharing Amperity data. |

|
|

|
Create the database in Snowflake from data that was shared from Amperity . Open the database, and then click the Get Data button. This opens the Get Data dialog box. Replace the value in the Database name field with the name of the database, and then choose the role, in addition to the ACCOUNTADMIN role, that have access to this database. Click Get Data. After the database is created click View Database. |
Verify table sharing¶
Verify that the tables shared from Amperity are available from a database in Snowflake.
To verify that tables were shared from Amperity to Snowflake

|
From the Snowsight user interface in Snowflake, expand Data, then expand Databases, and then find the database that was created for sharing Amperity data. |

|
Open the database, and then verify that the tables you shared from Amperity are available in the database. |