Google BigQuery¶
Amperity Bridge for Google BigQuery is a first-class integration that enables bi-directional data access between Amperity and Google BigQuery without copying data or scheduling ETL workloads.
What is BigQuery Sharing?
BigQuery Sharing publishes and shares datasets between organizations. Create an exchange, and then invite organizations to publish or subscribe to data in the exchange.
Note
Review Connect Amperity Bridge to Google BigQuery for more information about prerequisites, requirements, and optional configurations for Google BigQuery. All configuration prerequisites must be completed before stepping through this workflow.
To add an inbound bridge

|
On the Identity resolution page in Quick start, from the Add data source dropdown select Google BigQuery. 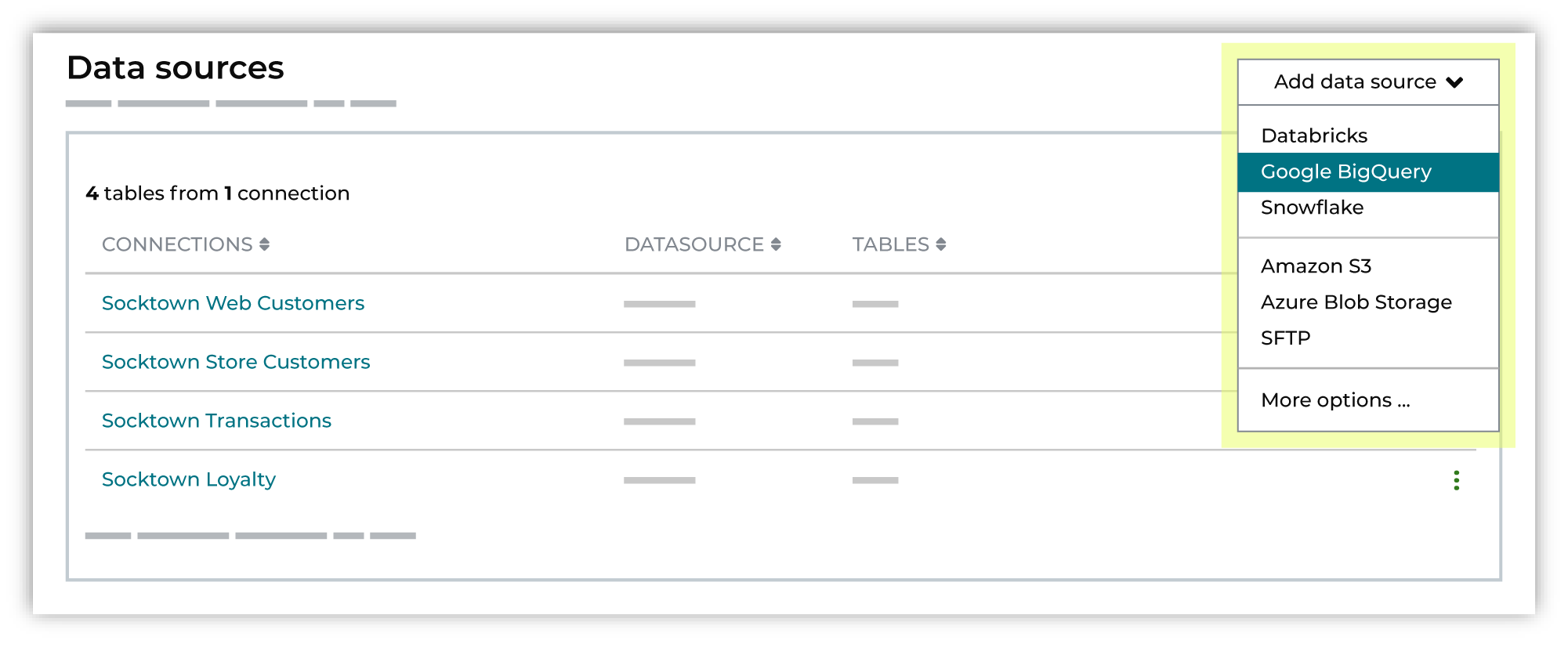
This opens the Add bridge dialog box. 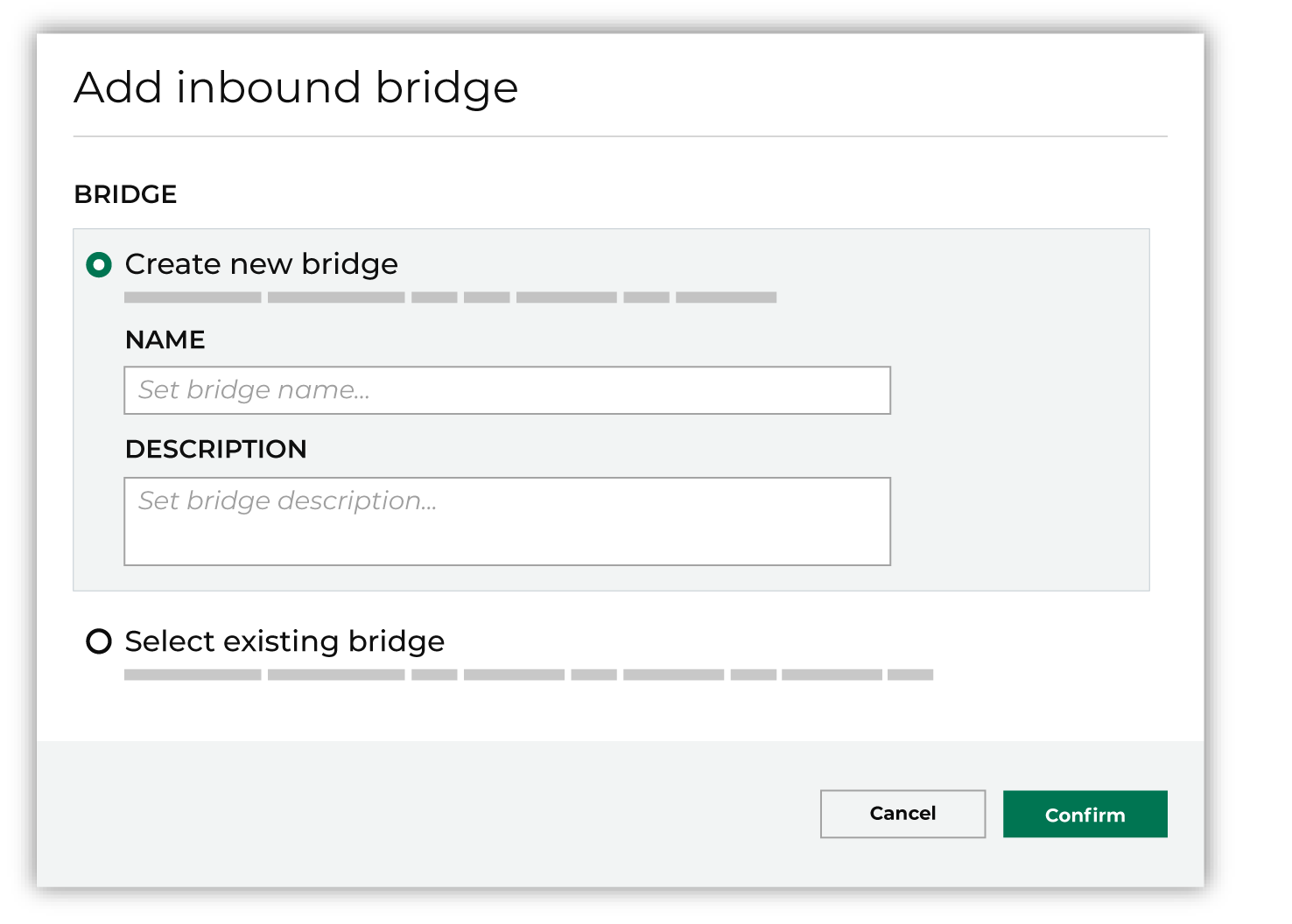
Add a name and description for the bridge or select an existing bridge, and then click Confirm. |

|
Add the share link that was copied from the Google BigQuery data exchange. Amperity generates the subscriber link after the share link has been configured. The share link is a URL similar to: https://console.cloud.google.com/bigquery/ \
analytics-hub/exchanges/projects/123456789012/ \
locations/<location>/dataExchanges/<exchange>/ \
listings/<listing>
Configure this identifier in Google BigQuery as the subscriber for the data listing. |

|
Use the Select tables dialog box to select any combination of schemas and tables to be connected to Amperity. 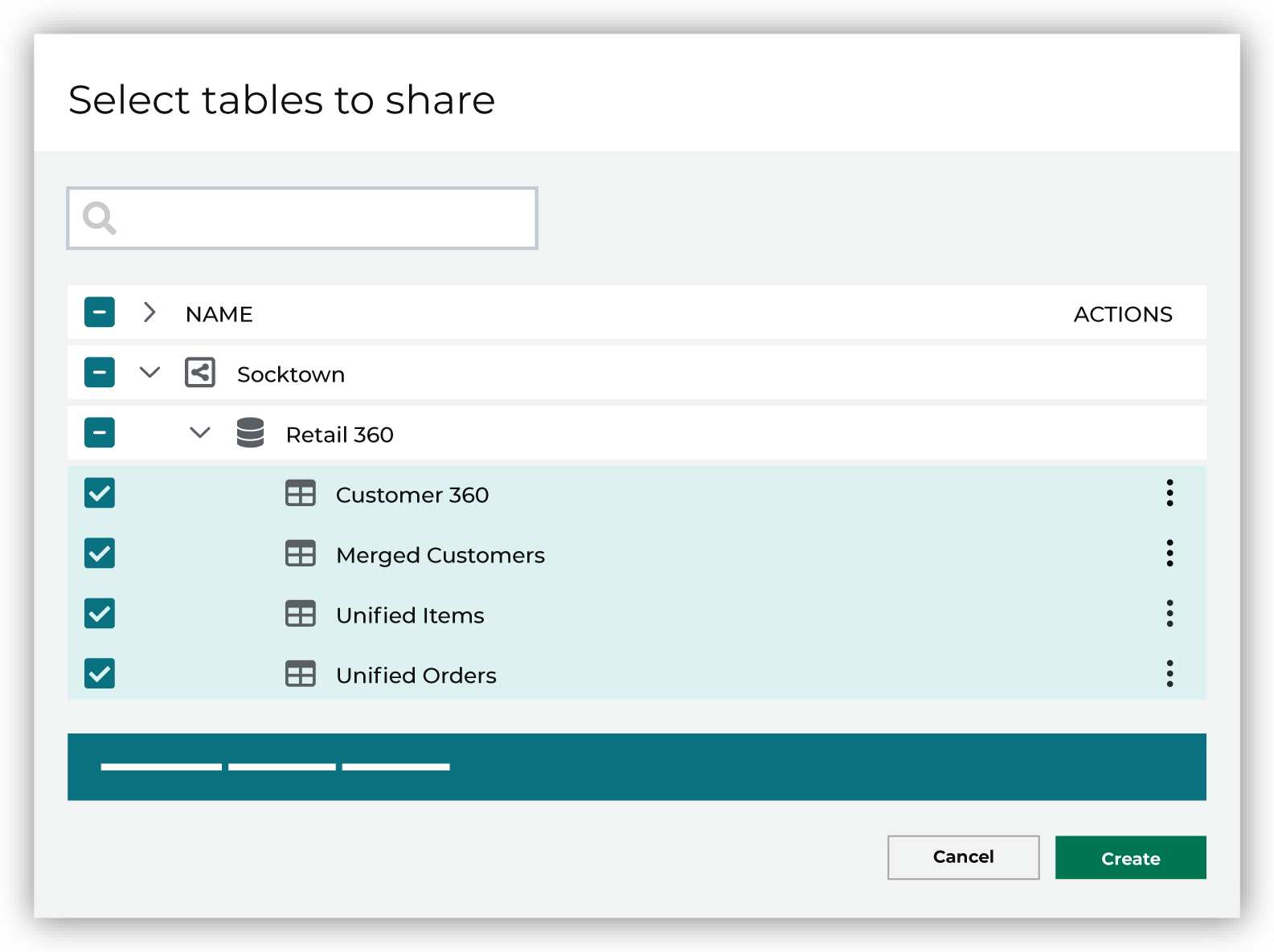
If you select a schema, all tables in that schema are connected. Any new tables added later need to manually added to the connection. When finished, click Next. This opens the Domain table mapping dialog box. |

|
Map the tables connected from Google BigQuery to domain tables in Amperity. 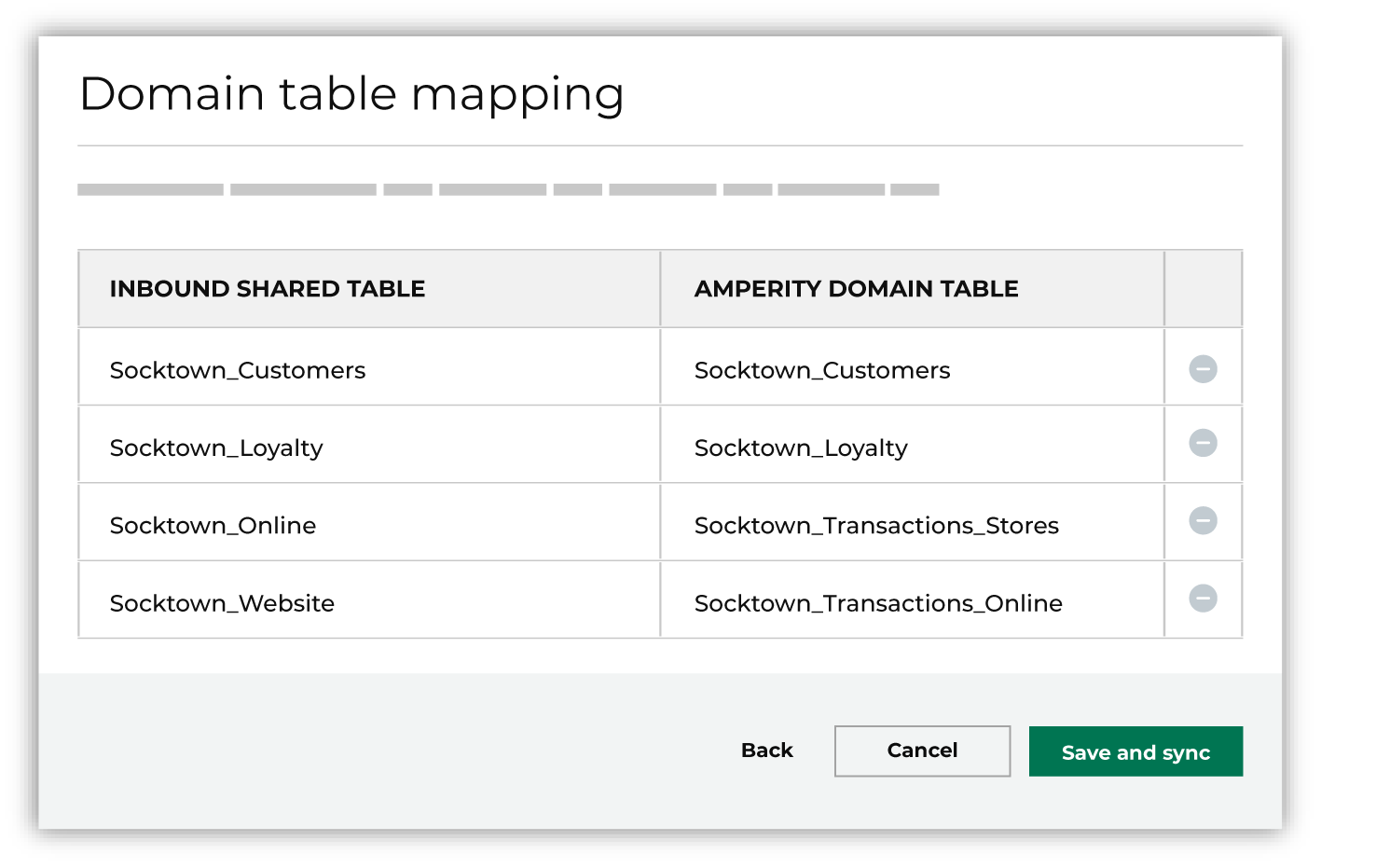
Tables connected with Amperity must have unique names among all domain tables. Primary keys are not assigned. Semantic tags are not applied. Tip Use a custom domain table to assign primary keys, apply semantic tags, and shape data within connected tables to the requirements of your workflows in Amperity. When finished, click Save and sync. This will start a workflow that synchronizes data from Google BigQuery to Amperity and creates the mapped table names. You can manually sync tables connected with Amperity using the Sync option from the Actions menu for the inbound bridge. |
Data types¶
Most Google BigQuery data types are supported by Amperity Bridge.
Important
If an upstream data type changes, edit the bridge in Amperity, accept the changes, and then save and sync the bridge.
Note
BYTES and RANGE data types are unsupported.
The following table describes how Google BigQuery data types map to Amperity data types.
Google BigQuery data type |
Amperity data type |
|---|---|
|
An ordered list of zero or more elements of non-array values. Each element must be a Google BigQuery type that maps to a supported Amperity type. |
Array An ordered list of zero or more elements of non-array values by field name and value. Fields within an Array must contain values for data types supported by Amperity. |
|
A numeric value and an alias for INT64. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values less than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
A decimal value with precision of 76. Important Amperity supports precision for BIGNUMERIC data types when they are less than or equal to 38. Precision that is greater than 38 is not supported. |
Decimal A fixed point number, such as for prices or message sizes. The number of characters in the decimal value is configurable. For example:
|
BOOLEAN , BOOL A value that can be TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. |
Boolean A value that can be TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. |
|
Variable-length binary data. |
Warning The Google BigQuery BYTES data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with BYTES data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A numeric value and an alias for INT64. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values less than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
A Gregorian calendar date, independent of time zone. |
Date An ISO-8601 compliant date value, such as a birthdate. For example:
|
|
A Gregorian date and time, as they might be displayed on a watch, independent of time zone. |
Datetime ISO-8601 compliant date and time values, such as a purchase or transaction, the time at which data was last updated, or a campaign launch date. For example:
|
|
A decimal value with a precision of 38 digits. |
Decimal A fixed point number, such as for prices or message sizes. The number of characters in the decimal value is configurable. For example:
|
|
An approximate double precision numeric value. |
Float A floating point number. For example:
|
|
A collection of points, linestrings, and polygons that represent a set or subset of the surface of the Earth. |
String A string of characters. |
|
A numeric value and an alias for INT64. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values less than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
A numeric value up to 64 bits. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values less than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
A numeric value and an alias for INT64. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values less than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
Represents JSON, a lightweight data-interchange format. |
String A string of characters. |
|
A decimal value with a precision of up to 38 digits. |
Decimal A fixed point number, such as for prices or message sizes. The number of characters in the decimal value is configurable. For example:
|
|
A contiguous range between two dates, datetimes, or timestamps. |
Warning The Google BigQuery RANGE data type is unsupported. Exclude fields with RANGE data types from tables before sharing them with Amperity. |
|
A numeric value and an alias for INT64. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values less than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|
|
Variable-length character data. |
String A sequence of characters, such as first and last names, email addresses, physical addresses, UUIDs and other IDs, phone numbers, ZIP codes, product names, and descriptions. May be empty. For example:
|
|
A container of ordered fields. Fields within a STRUCT must contain values for data types supported by Amperity. |
Struct A container of ordered fields by name and type. |
|
A time of day, as might be displayed on a clock, independent of a specific date and time zone. |
String A sequence of characters that represents the time of day. |
|
An absolute point in time, independent of any time zone or convention, such as daylight saving time (DST). |
Datetime ISO-8601 compliant date and time values, such as a purchase or transaction, the time at which data was last updated, or a campaign launch date. For example:
|
|
A numeric value and an alias for INT64. Note BIGINT, BYTEINT, INT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, and TINYINT data types are aliases for INT64 and represent values with fewer than 64 bits. |
Integer A numeric value, such as the quantity of items purchased. For example:
|