First purchase¶
First purchase returns a list of customers who made their first purchase during your chosen date range. For example, return all customers whose first purchase was during the previous 12 months:
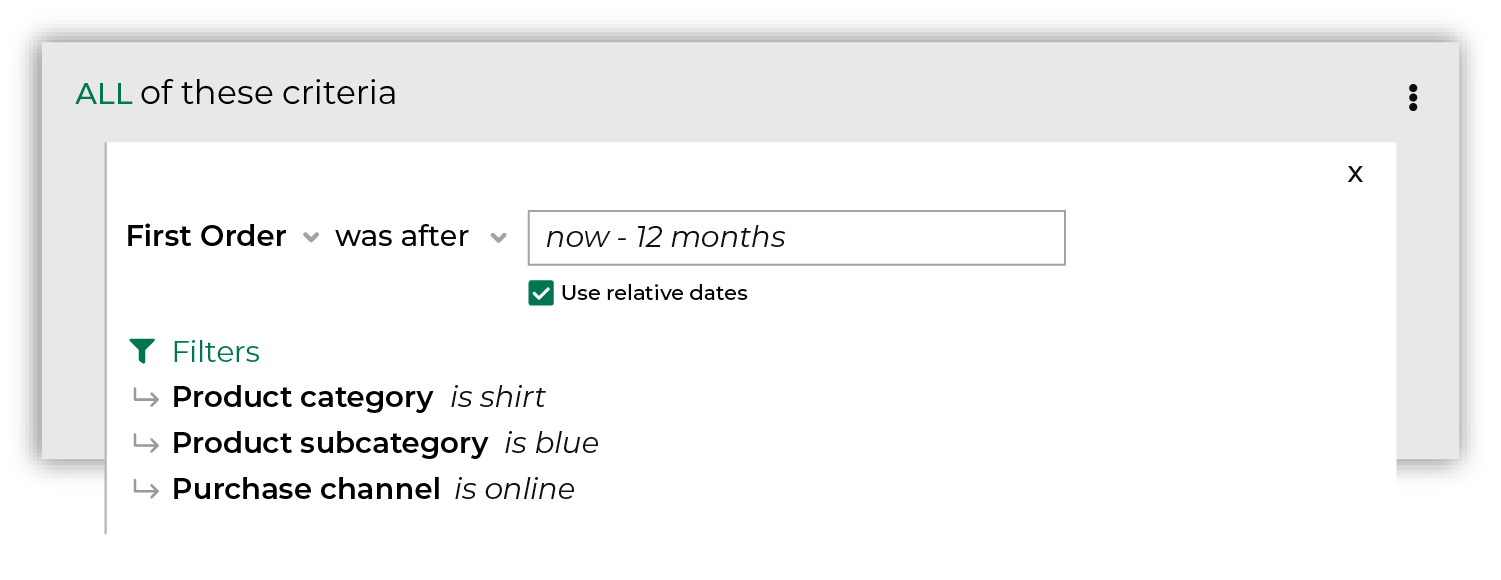
After you specify a date range you may apply filters to associate first purchases with specific products, brands, channels, and stores. For example, return all customers who purchased a blue shirt from your website.
How this attribute works¶
First purchase represents a common approach people use when they build segments: find all of my customers who made their first purchase in the past N days, months, or years, and then associate that list of customers to your products and brands.
First purchase is a compound attribute, which means that it is built from a combination of attributes that already exist in your data, and then appears as a single attribute that you can choose from the Segment Editor.
With this attribute, you can focus less on SQL and more on finding answers that align to your marketing goals and strategies. Purchase behavior attributes simplify the number of steps that are required to associate a list of customers to your products, stores, channels, and brands.
How does the SQL for First purchase work?
First purchase is built from standard columns that are output by Amperity. The following example returns a list of customers whose first purchase was a blue shirt that they purchased online within the previous 12 months:

The SQL for First purchase works like this. It uses order datetime from the Unified Itemized Transactions table as its starting point:
SELECT
amperity_id
,order_datetime
,RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY amperity_id ORDER BY order_datetime, order_id) AS order_rank
FROM Unified_Itemized_Transactions
then uses the RANK() function to identify which of those purchases were a customer’s first purchase, and then returns all items that match two conditions: order rank and a date range:
WHERE order_rank = 1
AND order_datetime > DATE_TRUNC('day', CURRENT_TIMESTAMP - interval '12' month)
In this example, only transactions that occurred within the previous 12 months and are a customer’s first purchase are returned.
Returns and cancellations are filtered out automatically, like this:
AND (is_return IS NULL OR (NOT is_return))
AND (is_cancellation IS NULL OR (NOT is_cancellation))
You may then filter this list of customers more by applying any of the product, purchase, and store filters. When you select these filters, they are added to the WHERE statement, like this:
AND product_category = 'shirt'
AND product_subcategory = 'blue'
AND purchase_channel = 'online'
and they are added to the SELECT statement, like this:
SELECT
unique_id
,order_datetime
,product_category
,product_subcategory
,purchase_channel
,RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY unique_id ORDER BY order_datetime, order_id) AS order_rank
FROM Transactions
WHERE product_category = 'shirt'
AND product_subcategory = 'blue'
AND purchase_channel = 'online'
Why are these attributes added to the WHERE statement and the SELECT statement? They are added to the SELECT statement to ensure that the correct ranking is applied to products, purchases, and stores before you apply product, purchase, and store filters to your segment.
The SQL for First purchase is more complex than what is described in the previous section. This is due to the way this attribute returns only a list of Amperity IDs, uses a series of common table expressions (CTEs), and takes advantage of workflows that Amperity does behind the scenes to pre-filter the product, purchase, and store attributes.
You can view the full SQL for First purchase from the Segment Editor. Start a new segment and add only this attribute (along with any required conditions and filter attributes), and then click the View SQL link at the top of the page.
Add to segments¶
You can add the First purchase behavior to a segment from the Segment Editor. Click Add condition, choose Purchase behaviors, and then select First purchase.

After the First purchase behavior attribute has been added, select an operator, and then finish defining the conditions for how this attribute should be applied to the segment.
About relative dates¶
A relative date is determined at the time a segment is run, where today is the day on which the segment is run. For example: yesterday, 30 days ago, 14 days ago, or 1 year ago. The list of relative date values includes a series of common ranges, but you may also type in a more specific range, such as 2 months ago or 5 days ago.
Relative date values
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
Tomorrow |
Starts at 12:00:00 AM of the day after the current day. For example, if the current day is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023” then tomorrow is “Friday 01 / 13 / 2023”. |
Today |
Starts at 12:00:00 AM or at the current time on the current day and continues for 24 hours. For example, if the current day is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023” then today is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023”. |
Yesterday |
Starts at 12:00:00 AM of the day before the current day. For example, if the current day is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023” then yesterday is “Wednesday 01 / 11 / 2023”. |
N days ago |
Starts at 12:00:00 AM of the day N days before the current day. For example, if the current day is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023”, then:
|
1 month ago |
Starts at 12:00:00 AM of the same day of the month that is 1 month before the current month. For example, if the current day is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023” then 1 month ago is “Monday 12 / 12 / 2022”. |
1 year ago |
Starts at 12:00:00 AM of same day of the year that is 1 year before the current year. For example, if the current day is “Thursday 01 / 12 / 2023” then 1 year ago is “Wednesday 01 / 12 / 2022”. |
Tip
You can compare segments by % of Purchasers, % of Revenue, or Revenue/Purchaser by changing the option in the Compare by: field.
Available operators¶
The following table lists the operators that are available to this attribute.
Note
Recommended operators for this attribute are identified with “ More useful” and operators with more limited use cases are identified with “ Less useful”.
Condition |
Description |
|---|---|
was after |
More useful Returns a list of customers whose first purchases were after the specified time window. |
was before |
More useful Returns a list of customers whose first purchases were before the specified time window. |
was between |
More useful Returns a list of customers whose first purchases were between two specified time windows. |
was not between |
Less useful Returns a list of customers whose first purchases were not between two specified time windows. |
was not on |
Less useful Returns a list of customers whose first purchases were not on the specified time. |
was on |
Returns a list of customers whose first purchases were on the specified time. |
Filter attributes¶
A filter attribute is a standard column that is output by Amperity and is available from the Unified Itemized Transactions table. When a filter attribute is associated with a purchase behavior attribute, you may use them to filter the results by specific items in your product catalog, such as by brand, by channel, by store, or by specific details about the items in your product catalog, such as color or SKU. The list of filter attributes that will be available for product catalogs depends on their availability within your Unified Itemized Transactions table.