About tools for analysts¶
Using Amperity for analytics requires being comfortable using SQL, including building databases and tables, designing queries, and using customer profile attributes and understanding what is required to synchronize results from Amperity to external systems and workflows that help your brand learn more about your customers.
Common workflows¶
The most common workflows for analysts within Amperity is a focus on data and databases, writing SQL to define queries and enable workflows, and interacting with attributes (both those output by Stitch and those generated by the ways semantic tags were applied to data sources in your tenant).
Use Amperity to:
Build your customer 360
Use SQL to define multiple databases, custom databases, and custom tables
Extend your customer 360 to make use of vertical-specific attributes and to define your own custom attributes
Explore data using the Data Explorer
The SQL query editor enable workflows, such as:
Linking the Amperity ID (first-party) to third-party provider person IDs
Enriching third-party non-PII data for customer analysis, segmentation, and targeting
Standardizing data for certain PII details
Using data hygiene to verify accuracy of PII with third-party data providers
Linking unknown IDs to known customers
Mapping unknown users to known customers
Mapping anonymous users to known customers
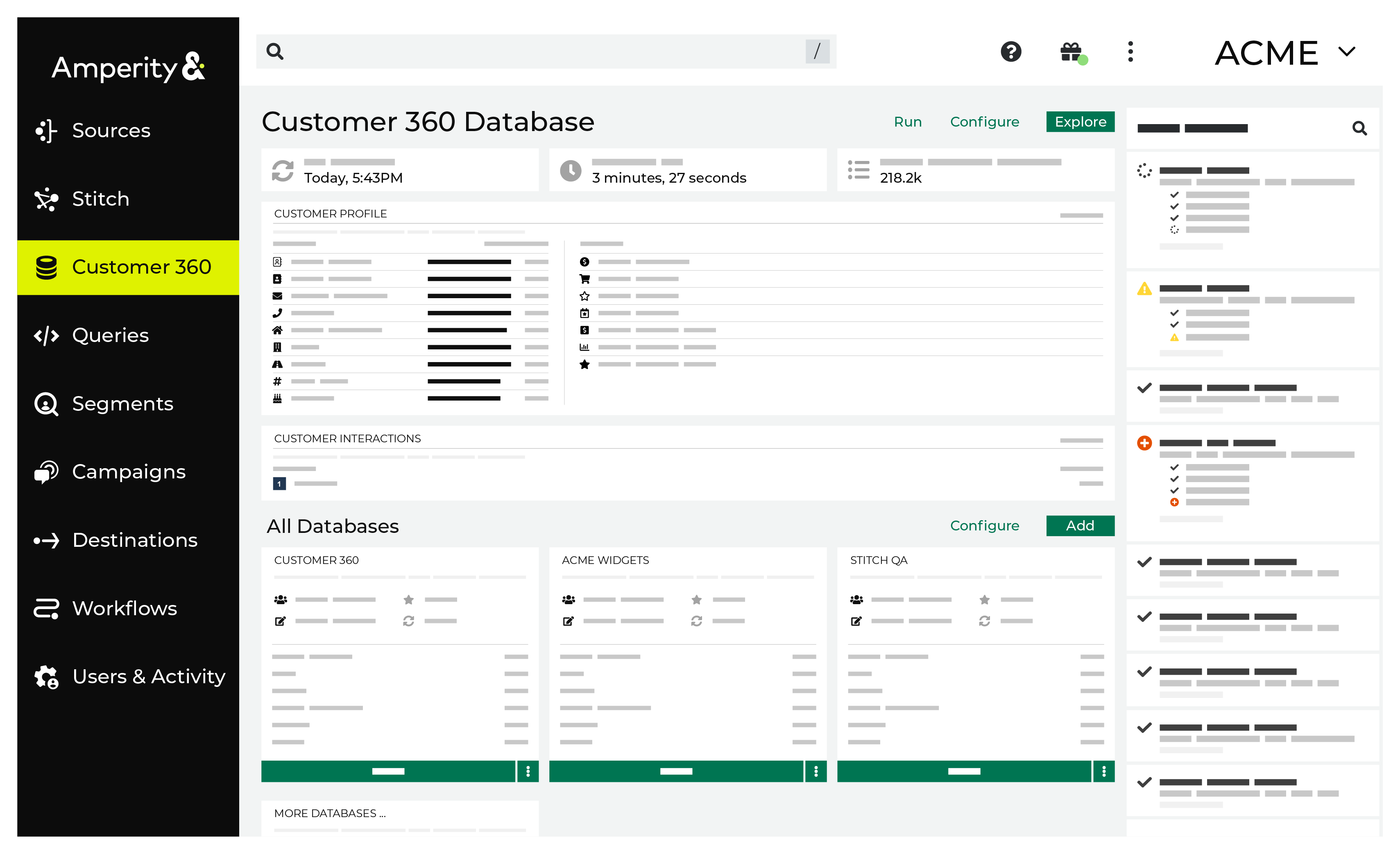
Customer 360 database¶
The customer 360 database is the most important database you can build in Amperity. It is the source from which all queries and segments are created and from which data will be sent to external systems for downstream workflows.
Flexible merge rules¶
Some customer data platforms require using an inflexible merge rule across multiple fields, which results in lower quality data across your customer 360 profile. This problem is magnified when that inflexible merge rule must also be applied to multiple customer 360 databases.
Amperity combines the use of flexible merge rules with a patented system that allows multiple customer 360 databases to exist within the same tenant. This ensures that:
Merge rules are 100% configurable
Each field can have its own merge rule
Each customer 360 database can have its own set of merge rules
Each tenant can support a variety of merge rules to meet all of the requirements for any individual use case
For example, data sources from call centers, online transactions, and email platforms may contain slightly different sets of customer profile data.
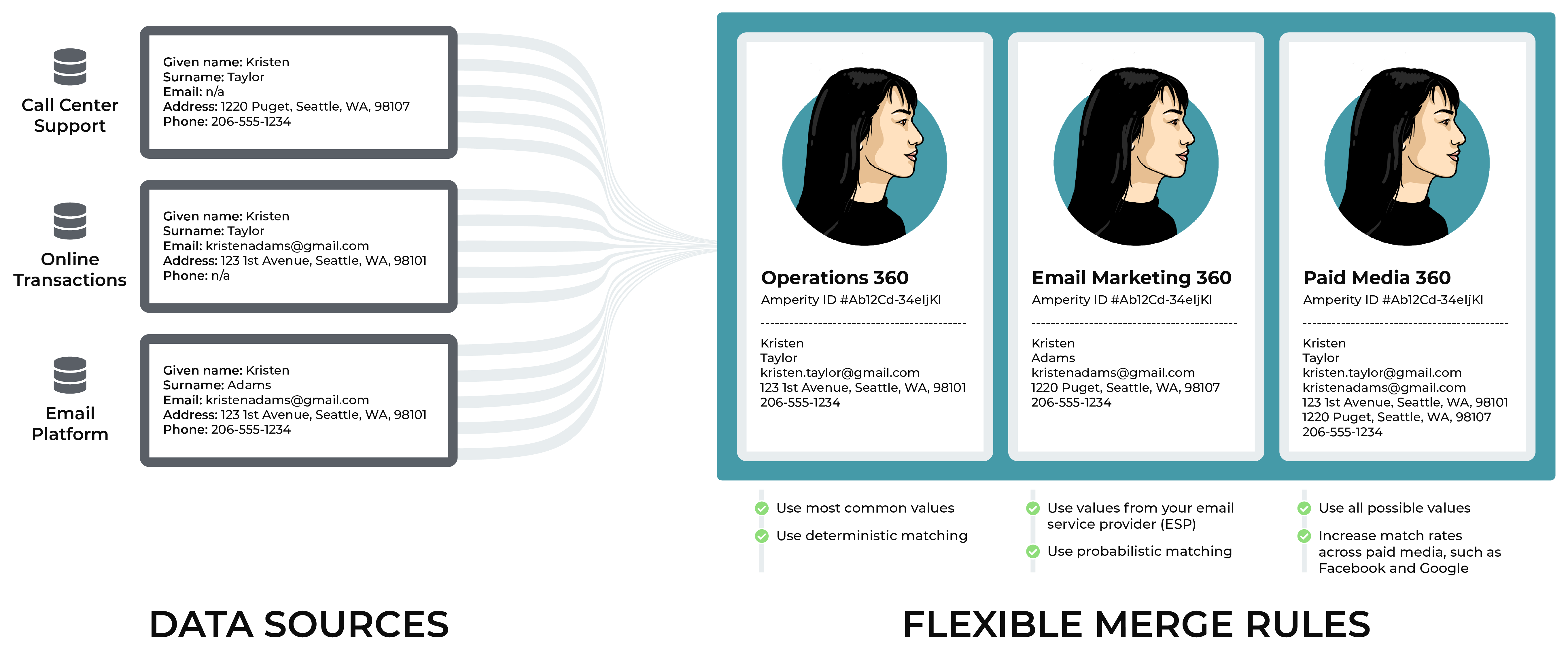
After loading this data to Amperity and assigning the Amperity ID to each of your customers, you can use flexible merge rules to support multiple customer 360 databases.
Your operations teams can combine prioritizing the most common values for each customer with deterministic matching
Your email marketing team can combine prioritizing customer profile values from your email platform with probabilistic matching
Your paid media team can combine all possible values to improve match rates on platforms like Google Ads and Facebook
Ask your Amperity implementation team for recommendations and best practices for how you can configure flexible merge rules to support all of your use cases.
Customer profiles¶
A customer profile is a collection of attributes connected to a single unique individual in the customer 360 database. The total number of customer profiles is equal to the total number of rows in the Customer 360 table. This total correlates strongly, but not exactly, with the total number of Amperity IDs assigned to unique individuals in the same dataset.
Customer profile details are pulled from the Customer 360 table that is located in your brand’s primary customer 360 database. Customer profile details include:
Names (first name, last name), email address, physical address, phone numbers
Transaction details (first purchases, last purchases, total purchases, etc.)
Other custom profile values that are unique to your company
These details can be accessed from the Profile tab on the Customer 360 page.
The Profiles tab shows the date on which the primary customer 360 database was last updated, how long it took to complete the update, and the number of customer profiles in the database.
Each customer profile is a collection of common attributes (first name, last name, email, phone, etc.), transaction attributes (first purchase, last purchase, total purchases, etc.), and other custom values that are unique to each customer’s data set. These details are summarized on the Customer 360 page under Customer Profile.
About the data model¶
The data model represents the “out-of-the-box” tables that are available to every tenant.
Important
This data model represents the starting point for all tenants. It is common for a tenant to have additional tables that support specific data requirements and workflows.
Data tables¶
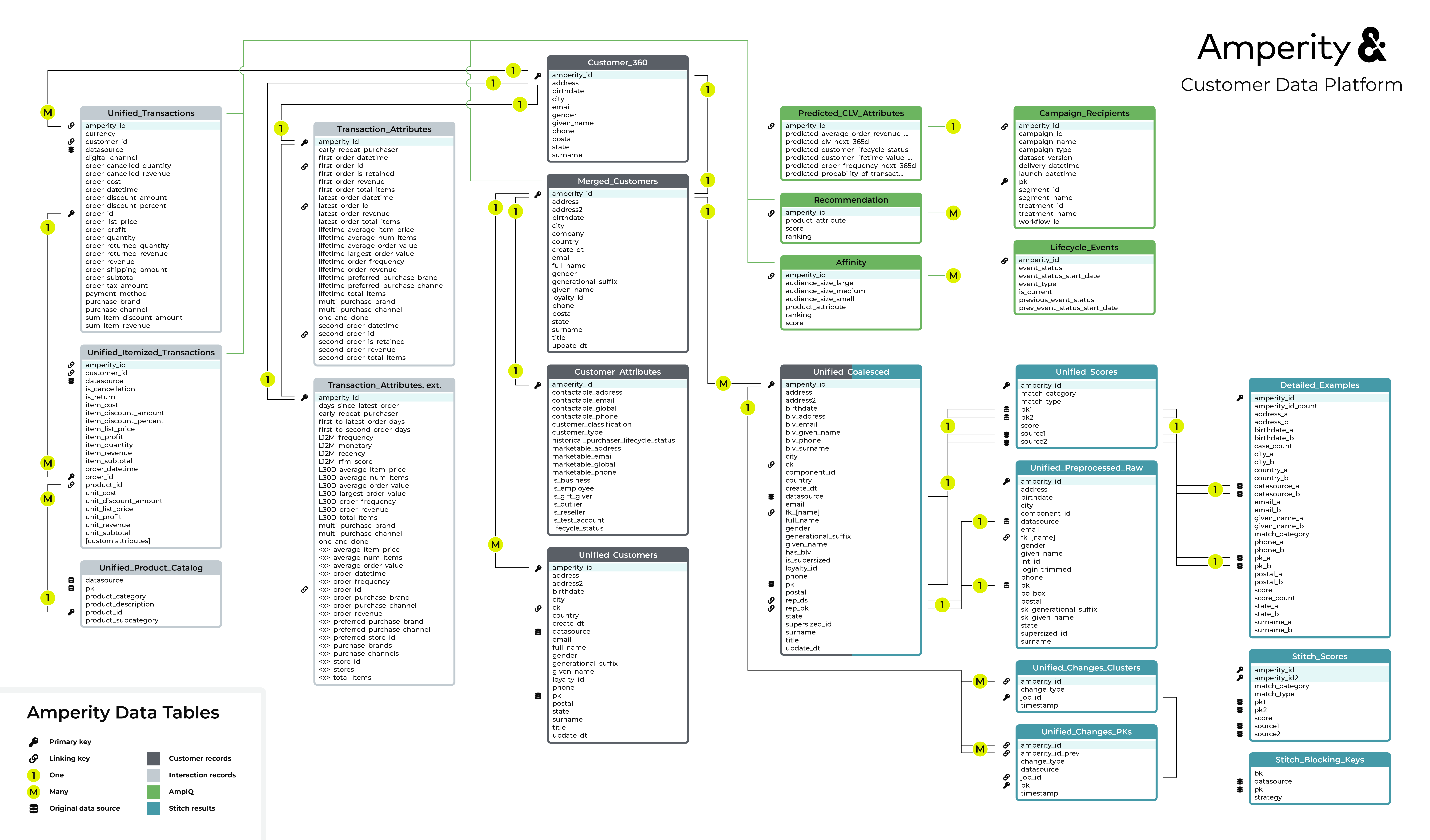
The following diagram shows the data model for core tables in Amperity. Color coded sections identify which groups of tables are associated with customer profiles, interactions records, Stitch QA, and predictive modeling.
Note
Click this diagram to open it in your full browser window. Click HERE to open this diagram in a new tab or right-click that link to save a copy to your computer.
There are four groups of tables in this diagram:
Group name |
Description |
|---|---|
Customer records 
|
A customer profile is a collection of attributes connected to a single unique individual in the customer 360 database. The total number of customer profiles is equal to the total number of rows in the Customer 360 table. This total correlates strongly, but not exactly, with the total number of Amperity IDs assigned to unique individuals in the same dataset. The Customer 360 table represents your primary set of customer profiles and is the most common starting point for building segments. Each customer profile is built using a combination of the Merged Customers, Unified Customer, and Unified Coalesced tables. |
Interaction records 
|
An interaction record is a row in a customer data table that has information about customer behavior. For example:
Interaction records rely on a series of tables: Transaction Attributes Extended, Unified Itemized Transactions, Unified Transactions, and Unified Product Catalog. Each Amperity ID in the Customer 360 table can be associated to many rows in the Unified Transactions table, and then each Amperity ID in the Unified Transactions can be associated to many rows in the Unified Itemized Transactions table. Each Amperity ID in the Customer 360 table is associated to one Amperity ID in the Transaction Attributes Extended table. |
Stitch results 
|
Stitch QA is a process that monitors the quality of Stitch results. Stitch QA has two parts: a database and a set of queries. Analyze the results to identify values for labeling, blocklisting, or to discover ways to tune the Stitch process to better match your tenant’s dataset. Stitch QA activities rely on a series of tables: Unified Coalesced, Unified Scores, Detailed Examples, Unified Preprocessed Raw, Unified Changes Clusters, and Unified Changes PKs. These tables are the basis for the Stitch QA process; the specific use of individual tables will vary from tenant to tenant. Together they provide visibility into how Amperity grouped (or did not group) individual customer records to a single Amperity ID. |
Predictive tables 
|
Tables may be enabled for users of Amperity. These tables rely on the Merged Customers, Unified Itemized Transactions, and Unified Transactions tables for predictions, but there is not a 1:1 or 1:many relationship between those three tables and tables. The Predicted CLV Attributes table contains one row per Amperity ID, whereas the Affinity and Recommendation tables contain many rows per Amperity ID. The Campaign Recipients table contains a history of all campaigns that have been sent from Amperity. This table is updated on a recurring basis and may be used like any other table in your customer 360 database. |
Data model indicators¶
This diagram uses the following indicators to highlight relationships between tables and to call out fields that are primary keys, establish links between tables, or associate this table back to a domain table in the Sources page:
Spark SQL¶
Spark SQL is a high performance SQL query engine used by Amperity to ingest data, create domain tables, and extend the outcome of the Stitch process within your customer profile database.
Queries¶
Queries enable you to discover lists of customers, get insight into their preferences and habits, identify properties and characteristics of that list, and then use that list to initiate marketing actions, campaigns, and other downstream workflows.
Queries also enable you to write SQL that can be used to perform QA against various databases and tables in the customer 360 database.
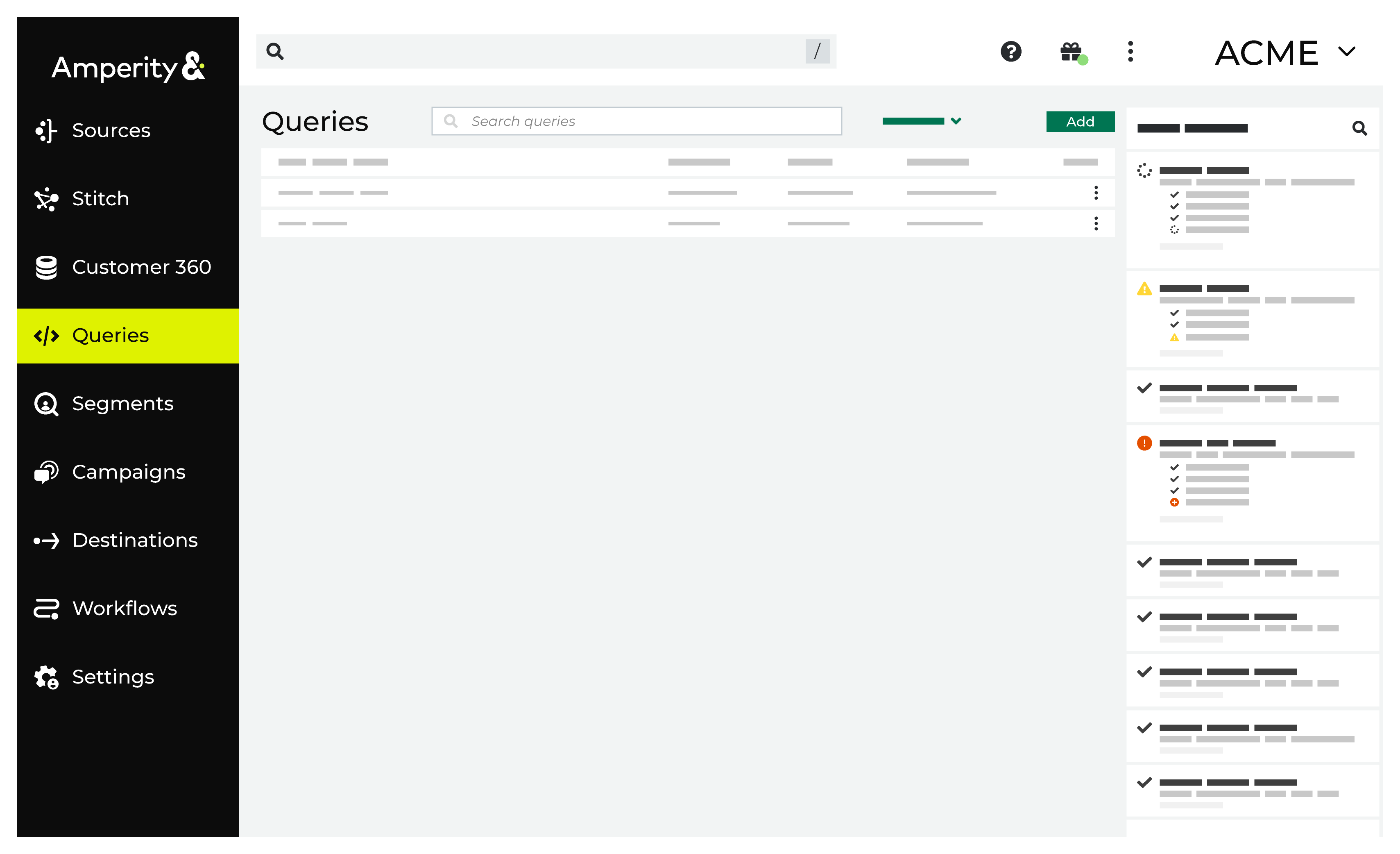
The Queries page provides a SQL interface for building queries. Use the visual editor to build queries with dropdowns and picklists. Use the SQL editor (and Presto SQL) to build more advanced queries. The Queries page keeps a list of all queries, in both active and draft states.
Both editors can access all tables in the customer 360 database, which contains all of your important customer attributes, along with passthrough tables that bring data that was pulled to Amperity from the domain tables to the customer 360.
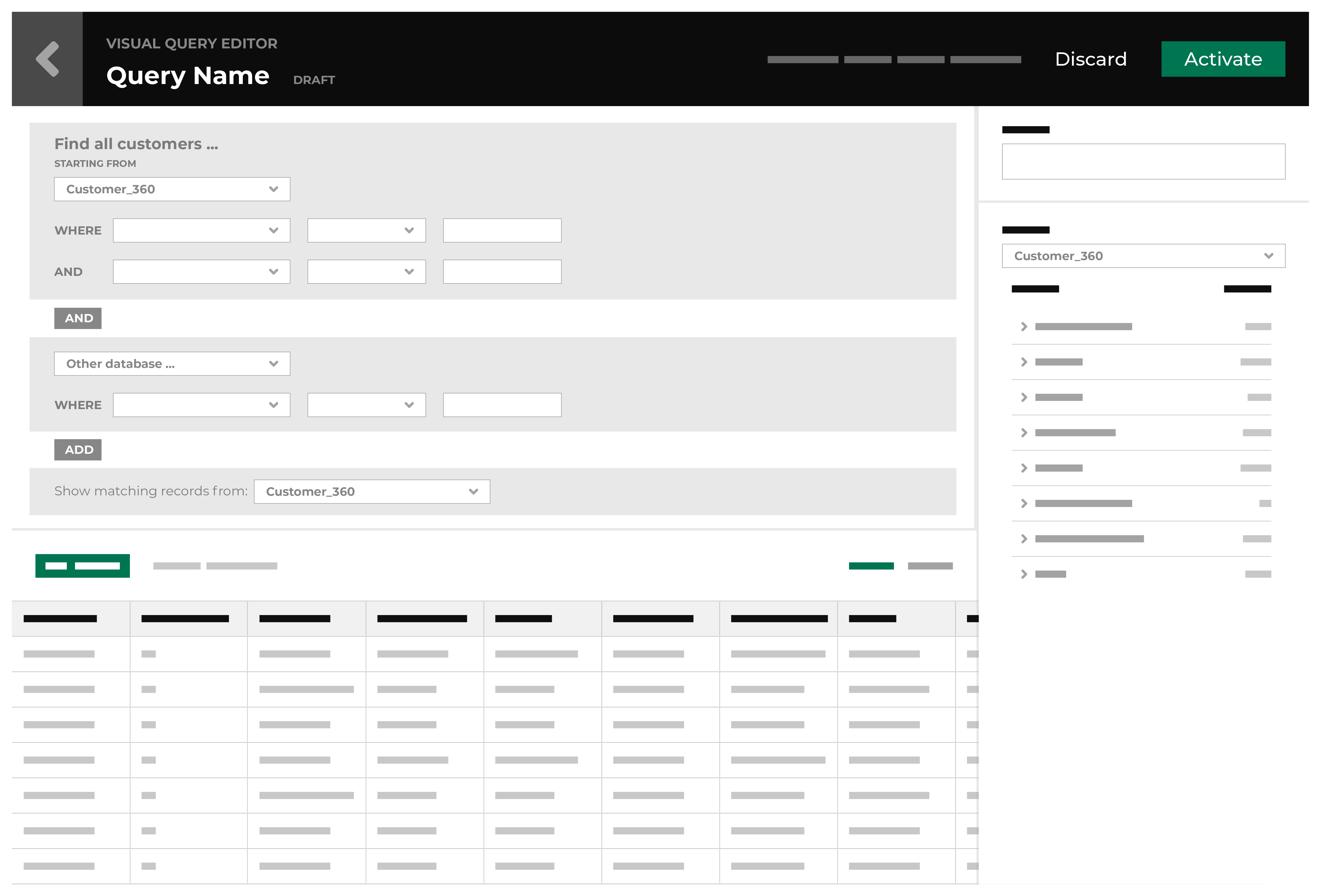
Query editor¶
The SQL Query Editor is the user interface for a full SQL query engine based on Presto SQL that interacts with customer database tables in Amperity. The SQL Query Editor relies primarily on using the SELECT statement, along with common table expressions, joins, functions, and other parts of Presto SQL to build and design advanced queries.
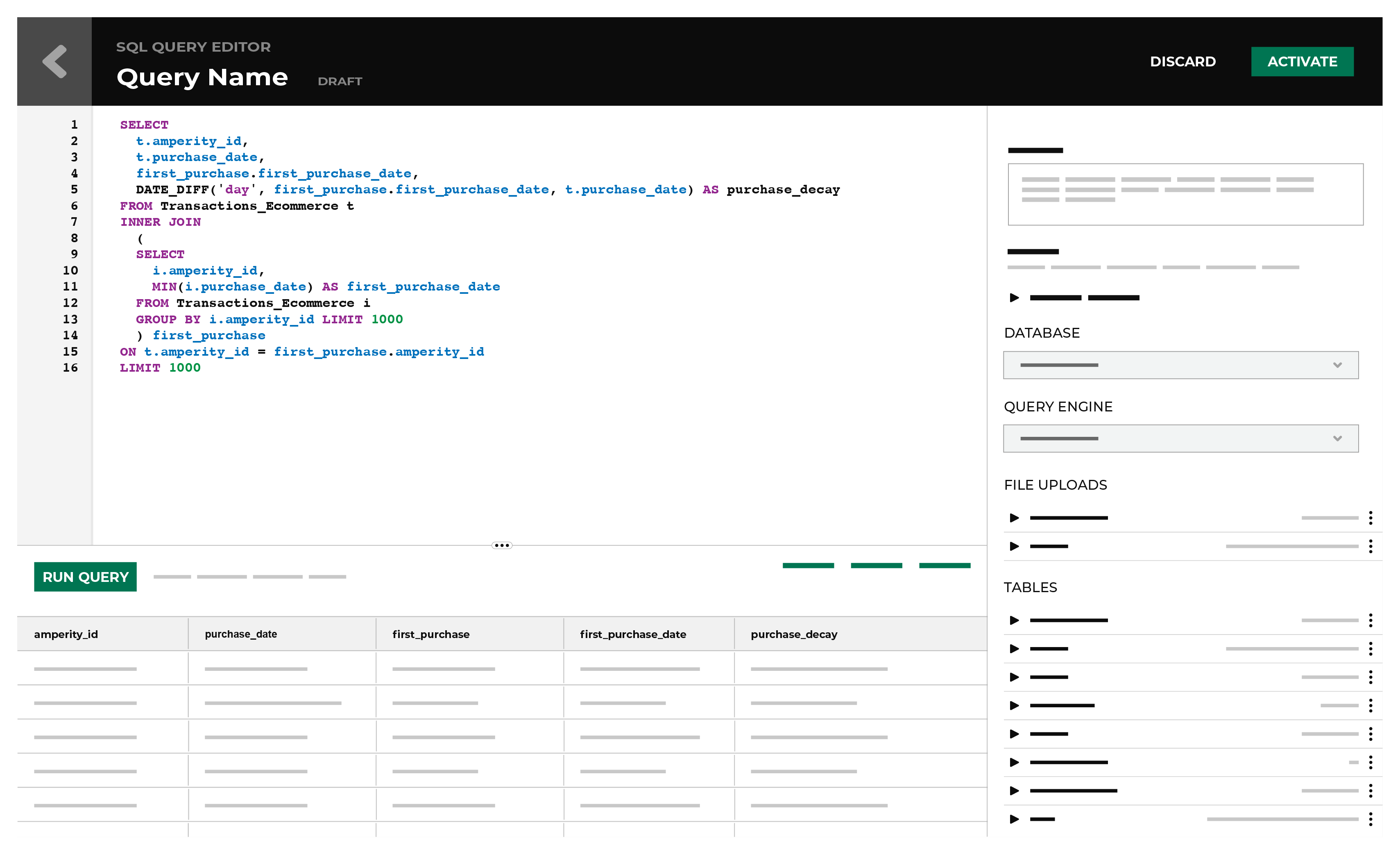
Presto is a distributed SQL query engine designed to efficiently query large amounts of data using distributed queries. The Queries and Segments pages use Presto to return query results and audience segments.
Because the SQL editor uses Presto SQL, you can also write any query directly as SQL.
Send to downstream workflows¶
You can send data from the customer 360 database to any downstream location or workflow. There are two ways to do send data:
By using Presto SQL to send only data that is returned by a query to a configured destination
By exporting a database or a table
Export databases and tables¶
A database may be configured to export one (or more) tables or an entire database from Amperity. Each data export must be assigned a unique name. A data export must be associated with a configured destination and must be added to an orchestration.
Sync with data lakehouses¶
Configure inbound and outbound shares in Amperity to enable bi-directional syncing of data tables between Amperity and Databricks and Amperity and Snowflake.
About this topic collection¶
The left-side navigation (from top to bottom) in this topic collection uses a verb-based approach to loosely organize around the series of actions that you may do when building queries, and then sending those results to downstream workflows.
The left-side navigation has sections for the following types of activities:
Reviewing Stitch results and ID resolution.
Viewing databases in the Customer 360 page.
Building queries using Presto SQL. These queries can support any desired use case.
Analyzing campaign results to support users of segments and campaigns.
Sending query results to any downstream workflow, including to BI tools such as Tableau, Microsoft Dynamics, and Business Intelligence Connect.
Example workflow¶
Amperity standard output tables provide the foundation for a complete view of your customer. Use queries to return any type of results, and then send those results to any destination.
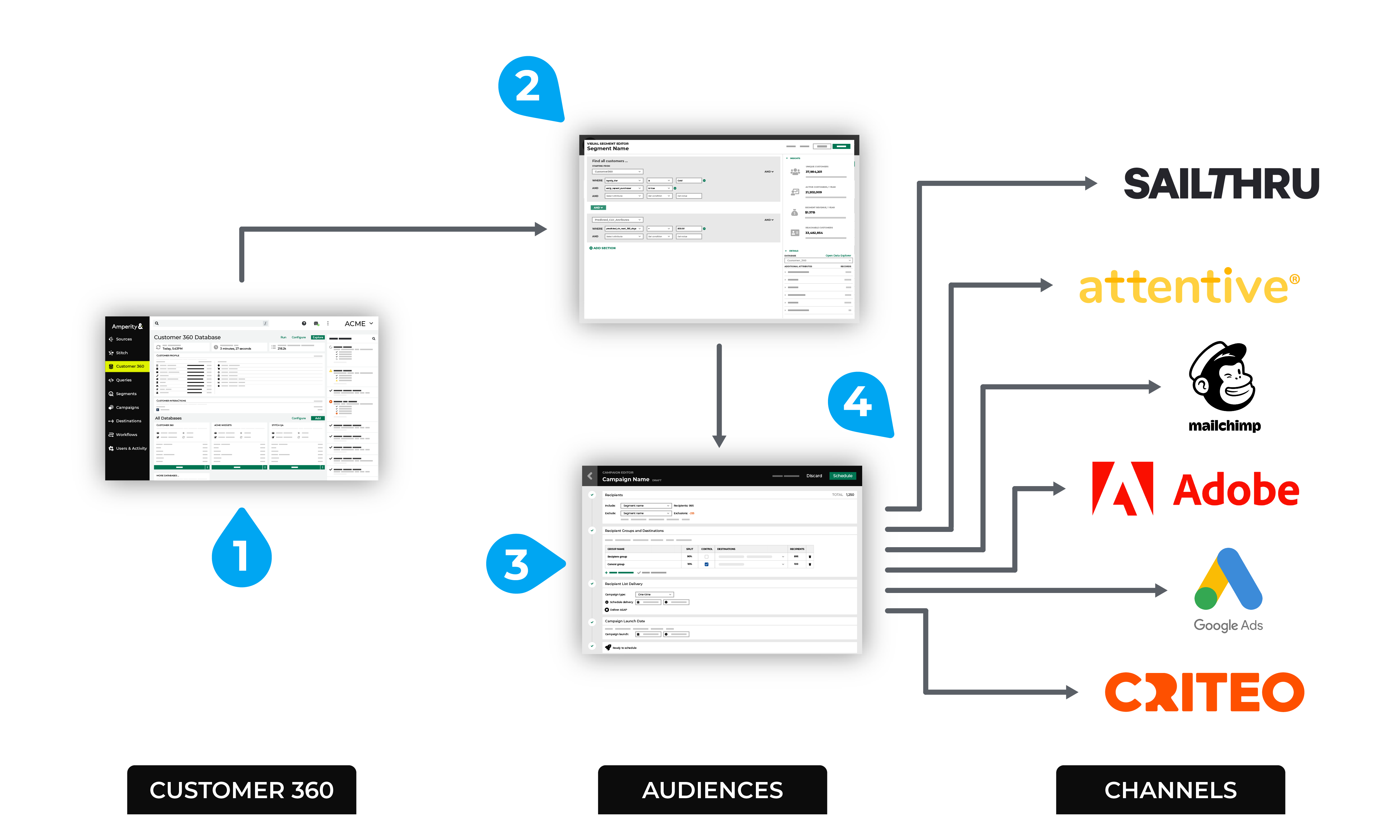
The numbers in the previous diagram represent a scenario that builds a query, and then sends results to a configured destination:
Open Amperity and review databases and tables.
Build a query that returns the right set of data to support your downstream workflow.
Send the results of that query to any configured destination. (Query results are sent to a single destination.)
Log in to Amperity¶
You must provide your credentials to Amperity in order to log in.
To log in to Amperity
Open https://app.amperity.com in your web browser. Google Chrome is recommended.
When prompted, provide your Amperity credentials.
Note
Most credentials are configured to use some form of single sign-on (SSO), but may be configured to use usernames and passwords, depending on how user access is configured for your tenant.
Click LOG IN.
Supported browsers¶
Amperity works best with Google Chrome and works fine with Chromium-based browsers, such as Brave.
Amperity is not supported from Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, or from mobile/tablet devices.